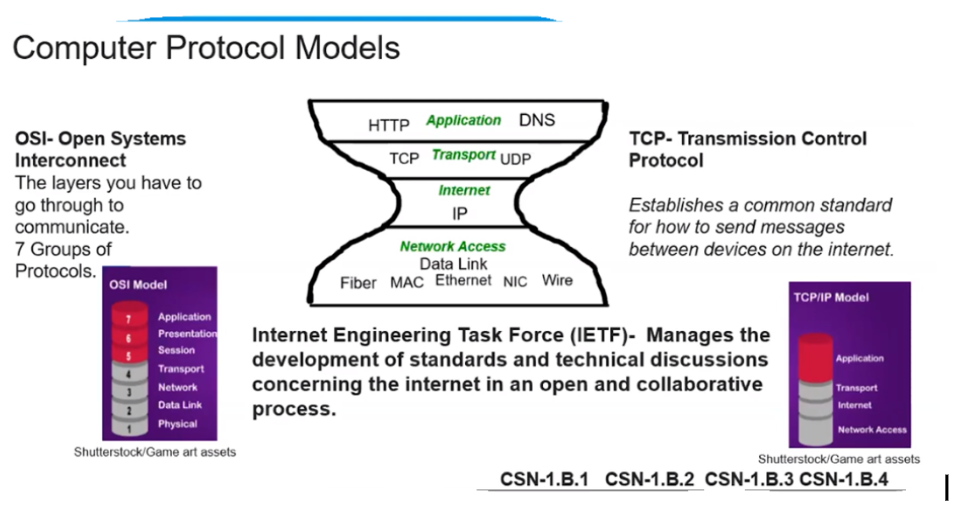
- Open systems Interconnect is a protocol model in which information can be transferred between the network.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol):
-Reliable Delivery: TCP makes sure that data sent between devices arrives safely and in the right order.
-
Connection Setup: Before sending data, TCP sets up a connection between devices.
-
Checks and Corrections: It double-checks to confirm data is sent and received correctly. If anything gets lost, it sends it again.
- Efficiency: It controls how fast data moves so that a fast sender doesn’t overwhelm a slow receiver.
TCP guarantees the safe and ordered delivery of data, similar to a registered mail service. It’s often used for applications like web browsing, email, file transfer, and etc.
-Overtime as computers became smaller, the users, or the people that are using the computers, want to send information across computers for various purposes
- A packet in networking is the idea that data is sent across a network in order to help “deliver” it. Each packet has a source (where it came from) and a destination (where it is going)
-ARPANET: One of the first net
-
A computer sytem is a group of computing devices and programs working together for a joint purpose
-
A computer network is a group of interconnected computing devices capable of sending or receiving data
-
Packet Switching: When a file is broken up into packets and sent in any order. The packets are reassembled by the recipient’s device
-
Routing is the pocess of finding a path form sender to reciver
-
A path is a sequence of directly connected computing devices that begins at the sneder and ends at the reciver
-
bandwidth: The speed at which data is sent on a compter network; measured in bits per second